The Data You Need to Know How to Preserve
Physical Paper Documents
Even if the world has shifted to a more digital landscape, some of the most sensitive business documents are still sheets of paper that can easily be stained, shredded, or misplaced; converting them into a digital format should be a priority.
Application Databases
Suppliers come and go; some applications do not integrate with others; but you still have to rely on them so making sure the databases they use are backed up is guaranteeing that the information they contain is in a format that can be re-purposed.
Computer Files
From emails to up-to-date office documents, files stored locally on computers are the most at risk as previous versions and older folders are often deleted to make room for newer content needed for the day-to-day business operations.
The Risks Associated with Unmanaged Data
Legal Compliance
Not managing data has become a business liability as regulations are becoming more and more demanding on how data is handled and failure to do so can result in hefty fines: you need to know what complying to PIPEDA, CASL, and GDPR entail.
Clients Protection
Clients data is vital to any business if centralizing it is a good way to make sure everyone has access to the latest information about a client; making sure this data is protected and cannot be used to harm a client is a responsibility.
Haphazard Curation
Managing goes beyond storing and keeping a record; curation is an integral part of the process.
Data should be organized in a manner that it would be easily searchable in order to find a document in a very short time.
Prevention Is Not Enough; These Will Happen
Data Deletion or Theft
Data Corruption
Servers Malfunction
Virus
Ransomware
Hack
The Most Effective Ways to Safekeep Your Data
Offline
External hard drives, USB keys, and cards are an easy way to safely store important files in a device that is not connected to the internet or a network which protects it from some of the most malicious issues.
Cloud
Online storage can be very convenient as it makes data accessible from virtually anywhere while being protected from issues that a compromised local enterprise network would face.
Offsite
It’s an offline backup that is staying at a location away from the office: home, bank, etc. Offsite backups should only be used as a backup of a backup; never as a go-to solution.
Avoiding a Single Point of Failure
Storage Devices Fail
If mechanical hard drives have a lifespan of 5-10 years for flash memory the lifespan is 300+ years but it is limited to 100K write/erase cycles. The bigger the drive, the more data at risk when it will fail.
No Internet = No Cloud
Cloud-based data solutions offer a lot of advantages but one major inconvenient is their lack of proximity and the reliance on servers that require a fast data connection and large bandwidth to be accessed which is not great when time is of the essence.
Sh*t Happens
A lot of things can happen to the location where an offsite backup is stored. Because it is a third option, it is often overlooked and neglected but as it is THE last resort option; it should be handled with care.
The Need for a Backup of a Backup of a Backup
Hot vs Cold Storage
There is a lot of strong data backup solution; however, not a single one of them is infallible. Using them in conjunction with one another is the only way to make sure your data is safe.
Redundancy in Planning
It is a good practice to check that data is indeed archived before being deleted and that the backup solution isn’t showing any symptom of an upcoming issue be it mechanical failure, storage running out of space, payment renewal, etc.
Making the Best of It
As they all have their advantages, the most important thing to remember is how to harness what they do the best to maximize the efficiency of your data management strategy.
These Factors Should Determine Your Strategy
Importance
Are these documents critical to your business?
What would be the fallout if this data was misplaced or lost?
Is there any scenario in which we would be required by law to produce these files?
Accessibility
How often do you need to have access to these documents?
How long do these files need to be available for?
In case of force majeure, how fast would we need this data to be at our disposal?
Risk
Do these documents need to be encrypted?
Is there a liability to these files falling into nefarious hands?
Are we under legal obligation to destroy this data after a certain amount of time?
The Key Concepts To Master Data Management
Hot vs Cold Storage
Hot means data that is used and updated on a regular basis and requires frequent backups. Cold storage is for archival data which retrieval can take several hours.
Redundancy in Planning
Having several plans with “what if” scenarios is the most effective way to prepare for unforeseen situations that may arise when encountering an issue with a data management solution.
Clear Accountability Chain
You need to know who is responsible for managing the data backups; who has ownership of the offsite backup solution; who has the decryption keys… and what redundancies are in place to avoid oversights.
Steps to Take When Updating or Upgrading
Backup Before Updating
Operating systems and applications often require to be updated; sometimes the process can go awry and the fall back protocol is to restore the OS at a previous working point which can entail a loss of the latest data so backup before updating.
Verify No Data Is Missing
Getting a new computer is always exciting; before completely abandoning the previous one, you should always make sure all the data needed has been moved to the latest device and obsolete content has been properly archived
Clean Before Recycling
Before disposing of an older computer; it is recommended to wipe its storage devices clean. This way if the machine ends up in someone’s hands, there is no possibility of confidential or personal information being stored on that device.
There Is No Reason to Have Orphaned Data
Emails and Contacts
Migration to a new email client or device is still one of the leading causes of loss when it comes to messages and contact info. This is why exporting them into archive files that can be imported or converted to work with a new system is favored.
Abandoned Databases
When switching to a new system that repurposes content from the database of the product it replaces, the database is often abandoned once the data is ported when it can still contain valuable information in fields that aren’t used by the new app.
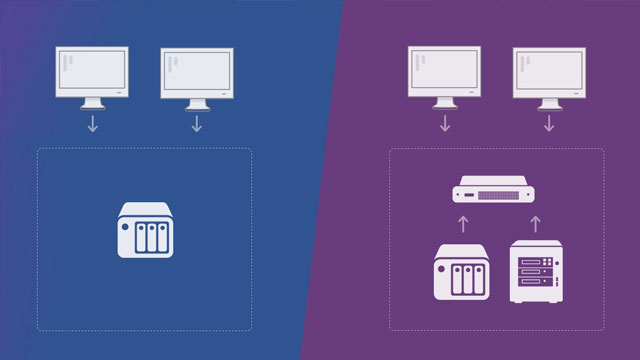
NAS and SAN
Network Attached Storage devices are a good solution to locally centralize and share documents for a business but it does create a single point of failure. Storage Area Networks offer redundancies but their cost is prohibitive and not worth it.